Viruses and bacteria are among the microscopic biological entities that can both be useful as well as harmful. Of the two, viruses are especially mind-boggling things. They lack almost everything to be counted among the living being. Nevertheless, viruses not only reproduce but they are, in fact, the most abundant bio-form on earth. Viruses are totally parasitic in nature. They hijack the cell machinery of the host to multiply. On the other hand, bacteria are single-celled living organisms that are capable of multiplying on their own without needing support from host. Likewise, there are a number of differences between virus and bacteria. Let’s have a look at these differences!
Virus vs Bacteria: Differences between Viruses and Bacteria
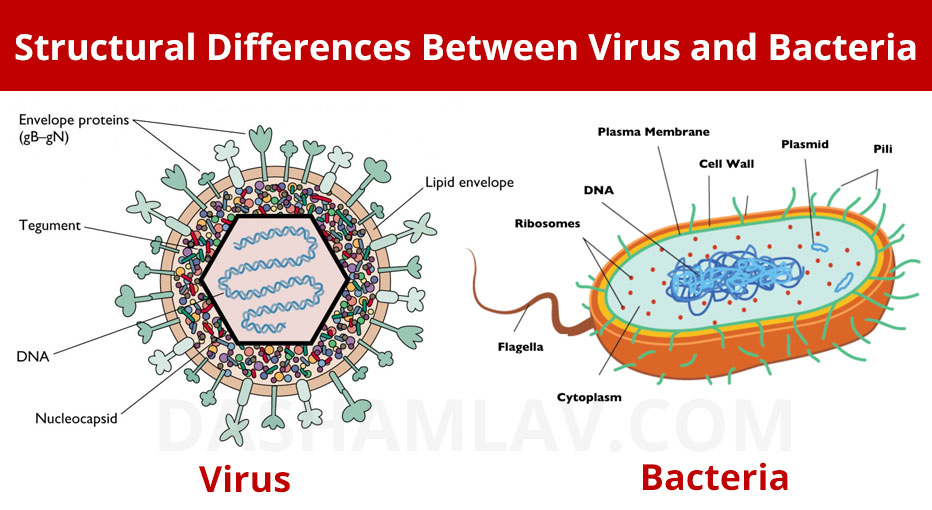
| Characteristic | Virus | Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Life | Viruses are considered non-living entities. | Bacteria are living single-celled organisms. |
| Reproduction | Viruses always need a host cell in order to multiply. | Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission. |
| Cell Wall | Cell wall is absent in viruses. Instead a protective protein coat called capsid is present. | Cell wall made of lipopolysaccharide or Peptidoglycan is present. |
| Size | Size of viruses varies between 20nm to 400nm. Viruses are visible only under electron microscope. | Comparatively bacteria are much bigger with size ranging between 800nm to 1000nm. Bacteria can be seen under light microscope. |
| Ribosomes | Absent in viruses. | Ribosomes are present in bacteria. |
| Genetic material | DNA or RNA remains encased inside capsid. | DNA or RNA floats freely in cytoplasm. |
| Metabolism | Viruses do not have any metabolic activities inside virus particles. | Bacteria show metabolic activities inside cell. |
| Harmfulness | Most viruses are harmful but some can be beneficial. | Only a small percentage of bacteria causes harm to human beings. |
| Infection | Viruses cause systemic infections. | Bacteria cause localized infections. |
| Diseases | Covid-19, AIDS, common cold, influenza, and chickenpox are examples of viral diseases. | Gastritis, food poisoning, ulcers, meningitis, and pneumonia are common bacterial diseases. |
| Treatment | Viral disease can only be prevented with vaccines. | Bacterial infections can be cured with antibiotic drugs. |
| Examples | SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, HIV, Poliovirus, Nipah are examples of viruses. | Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio cholera are examples of bacteria. |
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Virus vs Bacteria: Differences Between These Microscopic Entities." Dashamlav.com. Web. 12 June 2025. <https://dashamlav.com/virus-vs-bacteria-differences/>
Dashamlav.com, "Virus vs Bacteria: Differences Between These Microscopic Entities." Accessed 12 June 2025. https://dashamlav.com/virus-vs-bacteria-differences/
"Virus vs Bacteria: Differences Between These Microscopic Entities." (n.d.). Dashamlav.com. Retrieved 12 June 2025 from https://dashamlav.com/virus-vs-bacteria-differences/
