Orbit is the curved path in which an object in space revolves around another object or a celestial body, regularly and repeatedly. An orbit is usually elliptical in shape. But sometimes it can also be almost circular. For example, the moon revolves around Earth in an almost circular orbit while the orbital movement of Jupiter around the Sun is significantly elliptical when compared to that of the moon.
What is a Satellite?
Any object following an orbital path is called a satellite. Satellites can be of two types — natural or man-made. Moon is the only natural satellite of our planet Earth. Similarly, an artificial satellite launched from earth for purposes like telecommunication would be categorized as a man-made satellite.
Interestingly, while Earth has one natural satellite of its own, the number varies for different planets in our solar system. Terrestrial planets like Mercury and Venus have no natural satellite of their own. On the contrary, Jupiter has as many as 79 confirmed natural satellites.
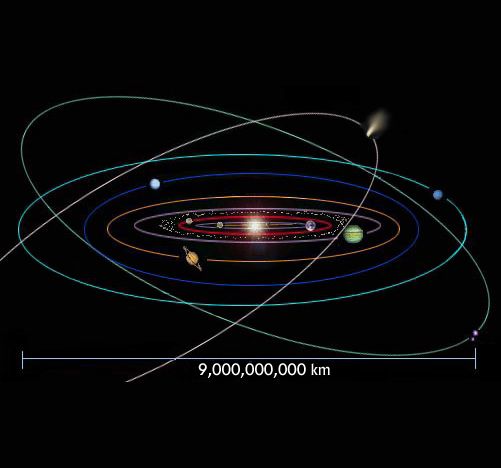
What makes an object in space follow an orbital path?
We all know that an object in motion continues to stay in motion unless it experiences a push or a pull. This is Newton’s first law of motion.
In space there is no air and therefore there is no air friction. So, if an object is set in motion, it will keep on traveling in a straight line unless it experiences another external force.
Now, let us take an example of Earth’s revolution. Moving planet Earth should have traveled in a straight line in space provided there exists no force pushing or pulling it. But Earth moves in a curved orbit. This means there is some force which is responsible for an elliptical curved movement of Earth. This force is gravity.
In space, every object with mass experiences an attraction towards all other objects nearby because of the gravitational force. This force of gravitation is directly proportional to the mass of two interacting objects.
In the present example, the Sun has greater mass in comparison to our Earth. This is the reason why Earth gets pulled towards the Sun. This gravitational pull accelerates the movement of Earth towards the Sun. As a result, Earth follows a curved orbital path for its revolution instead of moving away in a straight line.
Why doesn’t Earth get Completely Pulled into the Sun?
This is one question which often comes in people’s mind. Answer to this question is not that complicated. The Sun pulls Earth towards itself but the Earth is moving fast. Earth tries moving away in a straight line as a result of tangential velocity. But whenever it tries changing its trajectory of motion, it ends up getting pulled towards the sun due to force of gravitation.
Earth, thus, ends up following an almost circular orbital path while making an angle of almost 90 degrees with the Sun to the side of the direction it is moving. This is precisely the reason why Earth keeps on accelerating in its orbit without falling into the Sun. The same holds true for any two objects in space.
What is Barycenter?
Every object has a center of mass. To understand it simply, the center of mass is the point at which an object can be perfectly balanced. When we are referring to two objects in space, the common center of mass of both these objects is called the barycenter.
What is the relevance of barycenter in an objects ‘s orbital movement in space?
When two objects have similar mass in space, neither of them is at the center – as the gravitational pull is equal on either side. Thus, both the objects tend to revolve around each other. However, when there exists a difference in mass of the two objects – the barycenter is often closer to the center of the larger mass. Sometimes, almost within it.
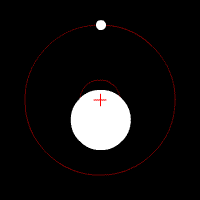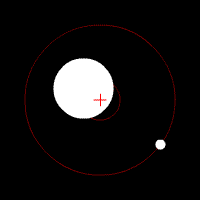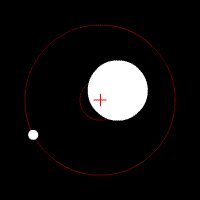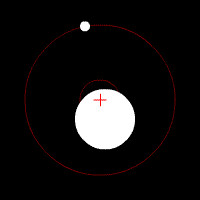
It is important to understand the concept of barycenter as we often believe that all the planets of our solar system revolves around the sun. Now this is not a completely correct statement. In reality, whenever we are referring to the sun and any planet, both the sun and that planet is revolving in an orbital path around the barycenter.
Oh yes, even the sun is moving around the barycenter. However, since the mass of the Sun is 99.8% of the solar system, the barycentre of most planets vis-a-vis the sun is often located very close to the center of the Sun.
Barycenter: Sun & Earth
For example, the difference between masses of Earth and the Sun is so huge, that the barycentre of these two celestial bodies is very close to the nucleus of the sun. As a result, despite following an orbital path – movement of the sun is not observed significantly.
Barycenter: Sun & Jupiter
The scenario turns different when we refer to the barycenter of the sun and the huge jovian planet Jupiter. The mass of Jupiter is only 318 times smaller than that of the sun. This results in a barycenter which is located outside the sun’s surface. Thus, the movement of the sun around the orbit in this particular orbit is more significant than that of the Earth’s.
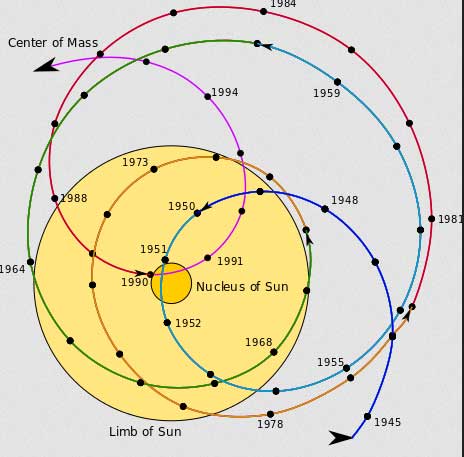
Barycenter of our solar system
The concept of barycenter is also applicable to more than two objects in space. Thus, our entire solar system also has a barycenter. Centre of mass of every object in our solar system cumulatively results in a barycenter of our solar system. Have a look at the picture below. It shows the barycenter of the solar system with respect to the Sun over the years.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"What is an Orbit? Meaning and Definition of an Orbit and Barycenter." Dashamlav.com. Web. 13 June 2025. <https://dashamlav.com/orbit-meaning-definition-barycenter/>
Dashamlav.com, "What is an Orbit? Meaning and Definition of an Orbit and Barycenter." Accessed 13 June 2025. https://dashamlav.com/orbit-meaning-definition-barycenter/
"What is an Orbit? Meaning and Definition of an Orbit and Barycenter." (n.d.). Dashamlav.com. Retrieved 13 June 2025 from https://dashamlav.com/orbit-meaning-definition-barycenter/
