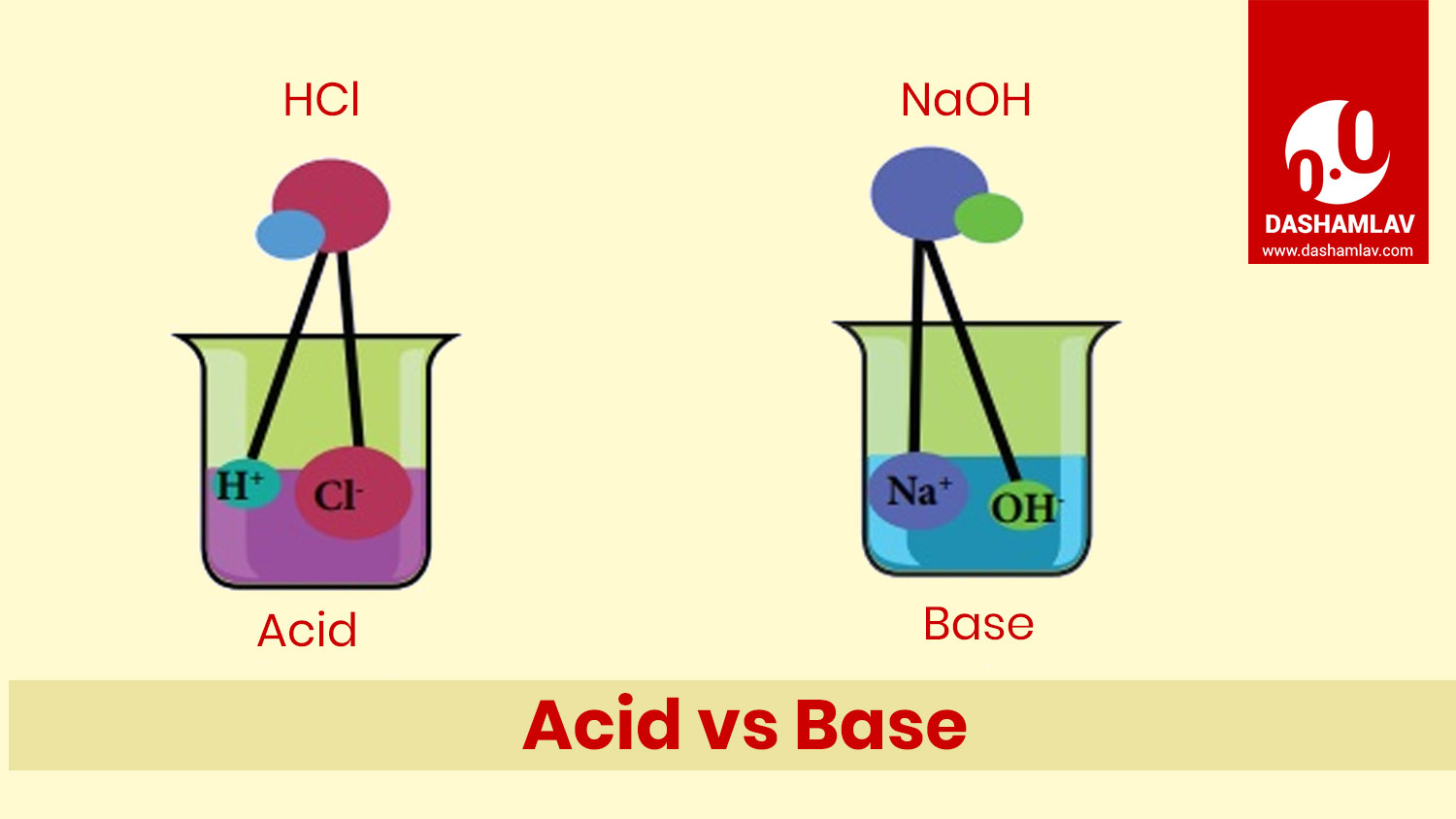
Acid and base are the chemicals opposite to each other. Both of these have significant roles in chemistry and are vastly present in our daily lives. A reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralizing reaction as they neutralize each other. Read on to understand the differences between the two.
| # | Basis of Difference | Acid | Base |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chemical Bonding | Acid is the substance that donates protons or accepts a pair of valence electrons to form a bond during chemical bonding. | The base is the substance that accepts protons or donates a pair of valence electrons to form a bond during chemical bonding. |
| 2. | Measurement of Strength | The strength of an acid is measured as its ability or tendency to lose a proton. | The strength of a base is measured as its ability or tendency to accept or gain proton. |
| 3. | Hydrogen ion (H+) | During a chemical reaction, acids donate hydrogen ions to the base. | During a chemical reaction, the base accepts hydrogen ions from acid. |
| 4. | pH (concentration of hydrogen ions) | When acid is dissolved in water it results in a solution that has hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water. This means the pH is less than 7.0. | When a base is dissolved in water it results in a solution that has hydrogen ion activity lesser than in pure water. This means the pH is higher than 7.0. |
| 5. | Taste | The taste of acid is sour. | The taste of bases is bitter. |
| 6. | State | Depending on the temperature, acids can occur in all three states – solid, liquid, and gas. | Bases normally occur in solid-state. Ammonia is one of the exception that occurs in the gaseous state. |
| 7. | Effect on Phenolphthalein | Phenolphthalein, an acid-base indicator, remains colorless with acid. | A basic solution changes the color of Phenolphthalein into pink. |
| 8. | Litmus test | Acids turn litmus paper or litmus solution to red color. | Bases change litmus paper or litmus solution to blue color. |
| 9. | Methyl Orange Test | An acidic solution turns methyl orange into red color. | Methyl orange remains orange with a basic solution. |
| 10. | Universal indicator test | Yellow and Red color in the universal indicator test indicates an acidic solution. | Blue and violet color in the universal indicator test indicates a basic solution. |
| 11. | Dissociation reaction | When mixed with water, acids dissociate hydrogen ions (H+). | When mixed with water, bases dissociate hydroxide ions (OH-). |
| 12. | Reaction with metals | When an acid reacts with metals it gives out H2 gas. | Bases do not react with metals. |
| 10. | Structure of Chemical Formulae | The chemical formulae of most of the acids begin with H e.g. HCl, HNO3, etc. Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is one of the exception. | The chemical formulae of bases end with OH e.g. NaOH, KOH, etc. |
| 11. | Strength | The strength of an acid depends on the concentration of hydrogen ions. | The strength of a base depends on the concentration of hydroxyl ions. |
| 12. | Physical features | Acids are corrosive in nature. | Bases feel slippery on fingers. |
Citation
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
Styles:
"Acid vs Base: Table of Differences between Acid and Base." Dashamlav.com. Web. 11 June 2025. <https://dashamlav.com/acid-vs-base/>
Dashamlav.com, "Acid vs Base: Table of Differences between Acid and Base." Accessed 11 June 2025. https://dashamlav.com/acid-vs-base/
"Acid vs Base: Table of Differences between Acid and Base." (n.d.). Dashamlav.com. Retrieved 11 June 2025 from https://dashamlav.com/acid-vs-base/