Bacteria are single-cell, prokaryotic microorganisms. While studying bacteria, it is important to classify them for information management purpose. There are several methods available to categories bacteria. These include simple methods like classification on the basis of cell shape, e.g. bacilli and cocci. We can also classify bacteria as per their growth in high or low oxygen environments. Gram staining is another method to classify bacteria on the basis of how bacteria retain the Gram stain. Hans Christian Gram, a danish biologist, developed the Gram stain. The Gram staining method also make bacteria more visible under a microscope. A bacteria can either be Gram-Positive or Gram-Negative.
Major Differences Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
| Basis of Comparison | Gram-Positive Bacteria | Gram-Negative Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Diagrams | 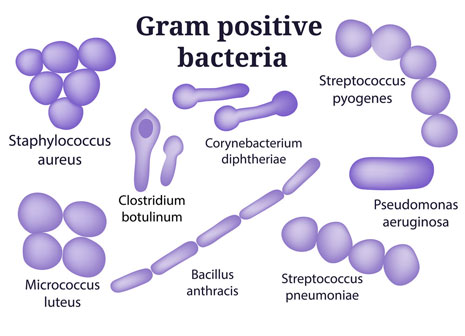 |
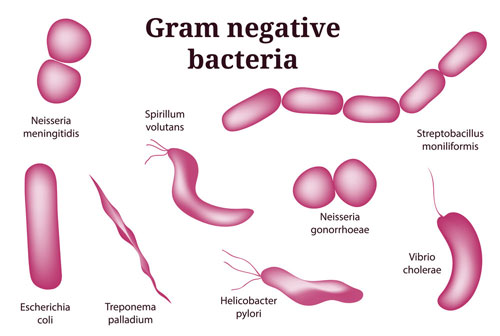 |
| Gram Staining | Stain blue or purple | Stain pink or red |
| Dye Retention |
Retain crystal violet dye | Retain safranin dye |
| Cell Wall | Single-layered and smooth | Double-layered and wavy |
| Thickness of Cell Wall | Thick (20-80 nm) | Thin (8-10 nm) |
| Peptidoglycan Layer | Thick and can be multilayered | Thin and often single-layered |
| Rigidity | Rigid | Relatively more elastic |
| Outer Membrane | Absent | Present |
| Periplasmic Space | Absent | Present |
| Lipopolysaccharide Content | Very low | High |
| Lipid Content | Low | 20 to 30% |
| Flagellar Structure | Two rings in basal body | Four rings in basal body |
| Magnetosomes | Usually absent | Sometimes present |
| Morphology | Usually cocci or spore forming rods | Non-spore forming rods |
| Toxin Production | Exotoxins | Endotoxins or Exotoxins |
| Pathogens | Only a few pathogenic bacteria are Gram-Positive | Most pathogenic bacteria are Gram-Negative |
| Inhibition by Basic Dyes | High | Low |
| Rendering | Can render Gram-Negative with increasing acidity | Can render Gram-Positive with increasing alkalinity |
| Examples | Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Clostridium, Enterococcus | Escherichia, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Helicobacter, Pseudomonas |
Gram-Negative bacteria offer more resistance to antibodies because their cell-wall is impenetrable.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Difference Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria." Dashamlav.com. Web. 27 July 2024. <https://dashamlav.com/gram-positive-vs-gram-negative-bacteria-differences/>
Dashamlav.com, "Difference Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria." Accessed 27 July 2024. https://dashamlav.com/gram-positive-vs-gram-negative-bacteria-differences/
"Difference Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria." (n.d.). Dashamlav.com. Retrieved 27 July 2024 from https://dashamlav.com/gram-positive-vs-gram-negative-bacteria-differences/
